Robotic process automation for enterprises is on the rise with no sign of slowing down. It’s many benefits, rapid return on investment, and customer and employee satisfaction have small, mid-sized, and large organizations starting their automation journeys. And you know what? Your competition is likely among them. Take the first step by familiarizing yourself with common RPA-related terms and their definitions.
A
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a technology capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. It is considered to be a simulation of human intelligence by the Robots. When we talk about AI in context of RPA – It gives organizations the ability to have end to end automation.
RPA works best with structured data – With the introduction of AI, Robots gets a capability to read the semi and the unstructured data, scanned documents, images. AI run on analytics and enhances the automations. Some Examples of AI are Text Classification, Image Moderation, Speech Recognition, Language translation etc.
Attended Robot
Attended RPA bots are like assistants working along with humans under supervision. These are the robots working inside the individual desktop. These robots have to be triggered by the human whenever required. They are mostly seen in front-end automation. Attended robots come in the picture whenever there is a human intervention required in between the process such as approving a transaction requiring decision making. Attended robots help individuals with small and repetitive tasks. The processes are triggered by the user. Users always have an option to provide the parameters to the process they want to trigger. These robots will be executed on the user machine only.

An example of the attended robot is available below where the customer support executive speaks to the customers, get their inputs, understand the query and create input data required by the robot. Executive will then trigger the attended robot; the robot will execute on the executive machine as per the instructions provided and generate the results.
C
Center of Excellence
RPA center of excellence is a group of experts that oversees all RPA initiatives across the organization. CoE enables organizations to manage the required capabilities to effectively implement RPA in any project. This group has people from varied experience such as project managers, RPA developers, citizen developers, business experts etc.
The primary role of the center of excellence is to set up a governance model across the company that all the automations project has to follow and comply with. It makes sure that required standards are maintained, takes care of the servers and licenses and runs various automation initiative across an organization. CoE makes sure that all the learnings and knowledge is accumulated and redistributed for future deployments.
CoE is required for:
• Organization of RPA Initiatives
• Maintain Governance
• Make sure to have the correct set of tools and technologies are available
• Guide the developers on automation approaches
• Take cares of the deployment environments
• Agree on set of responsibilities and helps in prioritization
• Embed the automation strategy
• Develop a roadmap for automation
• Embed resources learning plan
• Manage the technical aspects of technology
• Explore the latest tools and technologies
Concurrent Bot Execution
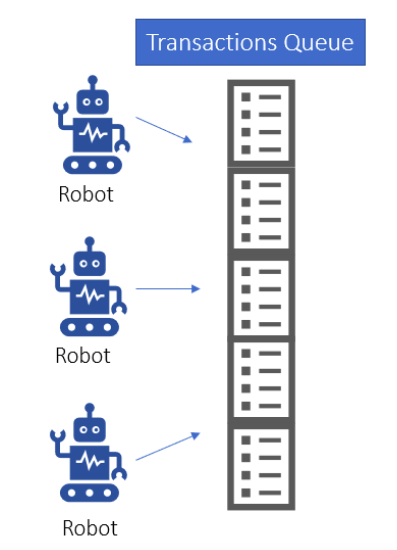
One of the major benefits of using robotic process automation technology is scaling. This means whenever the number of transactions in the process are increasing or decreasing, we need to scale the robots accordingly. Concurrent bot execution comes in picture when the number of transactions is more and each transaction is taking more time to complete. In such scenarios, we implement multiple robots to do the same process
Concurrent bot execution usually is implemented with the help of queues. Now multiple bonds are assigned to the same queue and with the help of a prebuilt mechanism the transactions from the queue are intelligently divided among the robots.
Citizen Developer
A citizen developer is a person who develops automations using low code or no code software. The term citizen imply that the developer does not have a background of software development and is more inclined towards the business.
Organizations use citizen developers to develop automations for business applications to be used by a particular department. These developers work under trained developers for guidance so the end product meets expectation. The concept of end-users creating their own solutions has potential impact of empowering citizen developers. Citizen developers only build new automations using pre-approved automation technologies. These automation solutions are used most often by an individual or at team level.
UiPath has a separate studio called StudioX which is targeted to the citizen developers. With StudioX, business users get a no-code platform to automate their mundane and repetitive tasks. It’s a no-code drag-and-drop construction, easy to code interface with pre-designed templates. StudioX has a native integration for enterprise application such as Microsoft office. Hence, day-to-day automation creation is easy.
D
Disaster Recovery (DR)
Disaster Recovery is an approach in Robotics which ensures that all the robots are working, the workstation are up and the processes are getting executed all the time. The robots are meant to be executed 24 X 7 and handle a huge volume of data which in terms means that there should be a high availability configuration.
• The factors which are ensured in the DR are
• Machines availability
• Network Connectivity
• Storage
• Adequate Licenses

It is important to setup DR as once the robots start execution – we have a business which is relying on the output of the robot. Technical failures with No DR would result to break the business continuity. One other important aspect of the DR is the recovery time which is calculated by time the services went down and the time they were restored back. In RPA, the recovery time becomes an important factor.
H
Hybrid Robot
In simple terms, hybrid automation is a combination of attended and unattended robots. Hybrid automation is useful when we require a human intervention in an unattended process. Part of the process is done by human interventions and decision making and other repetitive and mundane tasks are carried out by the robot. This allows robots to work in parallel with humans in a dynamic context.
Business processes that combine structured and unstructured data or an unattended process with decision points that require human intervention makes it eligible for hybrid automation. Hybrid automation approach help companies influence the power of automation in a more various range of processes and scenarios.
An Example of the hybrid automation is shown below where an unattended process is triggered, it downloads various files from sources and keep it in a folder for the human to have a validation. The Human comes in picture – validates the files kept by the robot, does the manual checks, and keeps the files ready for the next part of automation. The next part of automation again processes the files, generate the reports, and share the reports to the various stake holders
Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation is an approach that organizations use to identify and automate as many business processes as possible. Hyperautomation involves the composed use of multiple technologies, tools or platforms, such as:
• Robotic process automation (RPA)
• Artificial intelligence (AI)
• Machine learning
• Natural language processing (NLP)
• Chat Bots
• Integration to enterprise applications
• Low code platforms
• Task mining and Task capture tools
• Process discovery tools and technologies
• Optical character recognition (OCR)
It enables the wider organization audience to contribute to the one automation goal. It makes sure to have involvement of developers, testers, solution architects, project managers, citizen developers. It provides advanced analytics tools to measure performance and evaluate the return on investments.
Hypercare
Hypercare is a stage in the RPA development life cycle. Cnce the processes are deployed to the production, for some particular amount of time it requires a continuous monitoring as the robots are running for the first time in the live environment. This is the period where we anticipate some of the unexpected issues to occur. The robots are monitored and any defect is fixed as soon as possible.
The teams which are involved in Hypercare are the support team and the development. Depending upon the frequency of the process, the Hypercare can range from weeks to month. Once the business achieves the confidence that the process is running absolutely fine without any hiccups, the Hypercare is supposed to end and the process is marked as a Live process.
Training the business users regarding the new process is a critical aspect of Hypercare. As the system is new, initially it takes some time to get accomplished with the systems. All the findings, bugs, learnings are well documented. The next phase which comes after the Hypercare is the long-term support.
I
Intelligent Robot
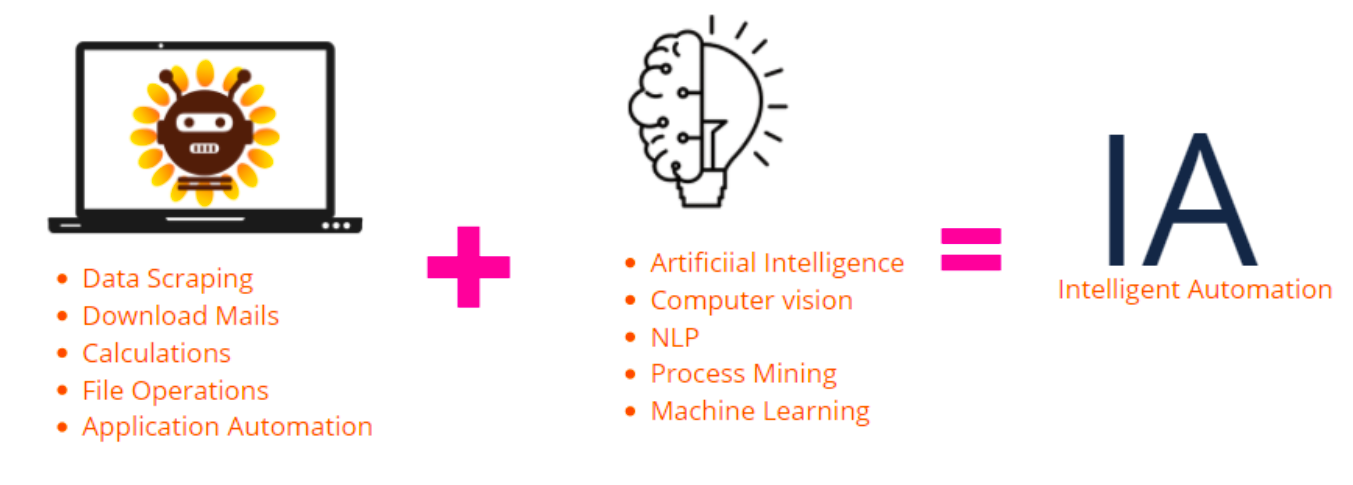
Intelligent automation is the combination of RPA with advanced technologies such Artificial Intelligence (AI), Optical character recognition (OCR), Cognitive Technologies, Computer vision etc. With the help of intelligent automations and use of analytics, we can have solutions with automated decisions providing more flexibility to the end-to-end automation.
The primary objective of intelligent automation is to improve the end customer experience, reducing manual interventions in the automation cycle and making automated decisions.
With IA, we can have flexible, resilient, and modern automation solutions with no human intervention. IA provide the capability to automate a business process end to end, improving the customer experience and saving more cost. Input format of data is no longer a challenge. With IA, we can read semi- structured and unstructured data that increase the scope of the automation in the organization. It decreases or eliminates the exceptions created by the automated processes as the robots learn and handle exception on its own.
P
Process Mining
Process Mining is an analysis which is done at the enterprise level by investigating the server logs, larger data sets and aims to automate the end-to-end business process and not just a task. A process consists of sequence of tasks which are when performed together completes the process. Process Mining would be dividing the process into sub processes and each sub process again having a set of tasks.
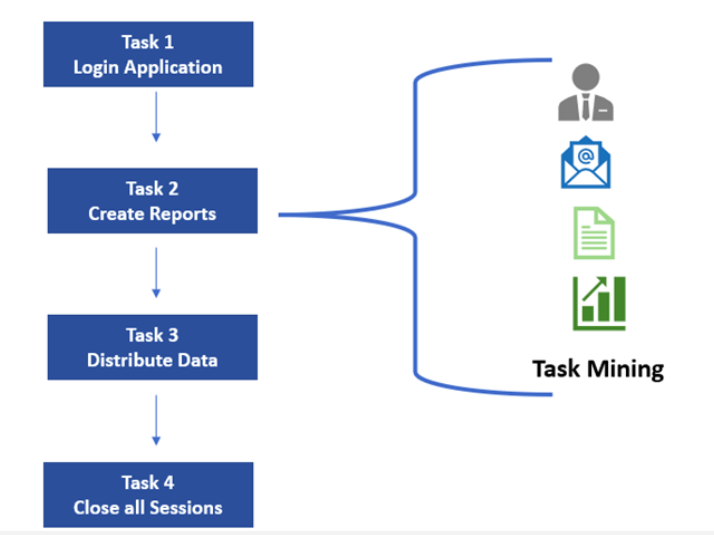
For Example: Below diagram depicts a complete process of report generation which are having at 4 tasks to be completed. when all the 4 tasks re completed in an order the process gets completed. Process Mining is the getting these details out of the Process. Each task can now have a separate set of steps extracted using the task Mining.
Proof of Concept (PoC)
Proof of Concept means a prototype of the actual automation. POC is usually created to test the capability of the automation tool. This is not a part of actual automation and cannot be used for delivery. POC is the first step for organizations who like to experience the RPA for process automations.
A POC allows you to observe an automation working with existing systems, applications, and data in their respective environments. It also provides an opportunity to validate the software or platform opted for the automation. POCs are quick to implement and deploy. A POC will always have a clear objective, defined start date and end date, will have the relevant test data and environments available. In terms of business benefits, the business does not actually have to onboard the complete solution, only minimal software’s and tools has to be onboarded.
R
Robot
When we refer to robot in RPA, we mean the software robot. We are not talking about the walking, talking robots. We mean a program which is running inside our computer and doing the mundane task for us. Robots mimic a human worker by completing such tasks as logging into applications, entering data, calculating, transfer files and folders, copy and paste data, extract structured, semi-structured and unstructured information from documents, and more. Software robots are flexible and are capable of doing tedious work at much higher pace and accuracy.

S
Structured Data
Structured data is highly organized and have a defined structure or model. It is easy to use and do the data manipulation. We can easily query and interpret the structured data. An example is a Table of data having rows and columns which we have extracted from a Database.

T
Task Mining
Task Mining is the technology which allows CoE to understand how the processes are being executed in the organizations. This is usually done by monitoring the user interactions across applications and collecting the input and output from day-to-day operations. Data collected from Task Mining is then analyzed for repetitiveness and optimization. Processes are optimized and the potential candidates for automations are identified.
Task Mining often makes use of technologies such as OCR (Optical Character Recognition), NLP (Natural Language Processing), AI (Artificial Intelligence). Main purpose of the Task Mining is to record the process which the employee is doing. For Example: A Task for an Employee can as simple as Reading the Emails, Downloading the attachments and creating the reports out of it.

U
Unattended Robot
Unattended robots are the ones with the capability to run in background without human intervention or supervision. These robots are scheduled to run at a particular time. These are used for repetitive and transactional based process. These required elevated rights and access to the application. The end user directly gets the final output at a stipulated time without any intervention.
Unattended robots do not need direct user interaction to trigger an automation. It runs on dedicated machines; the user does not need to interrupt their work for triggering a task/process. Unattended robots are scheduled to run on timely basis such as hourly/daily/weekly. Back-office automations are good candidates for the unattended robots.
An example of the unattended robot is shown below where the unattended robot will schedule as per the trigger, download the files from various sources and keep it in a folder. Robot does the processing and generate results and share the results to the designated users.

Unstructured Data
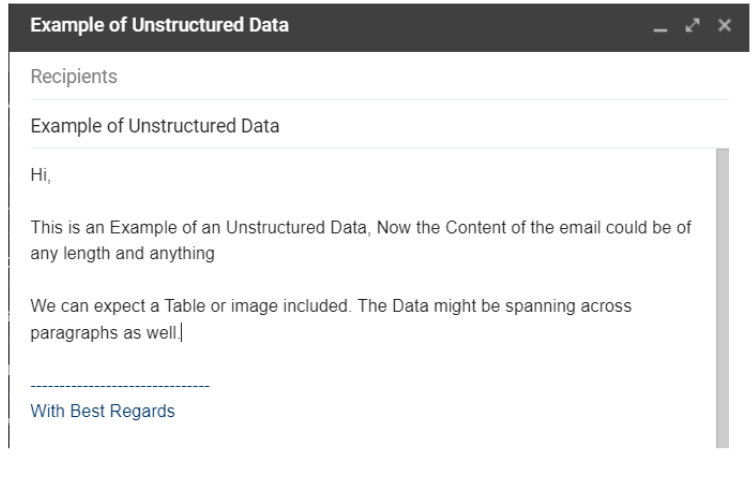
Unstructured data does not have a predefined model. It is difficult to use and interpret the data. For querying the unstructured data, it first has to be converted to structured data. A good example would be an email which can be any length, any number or any types of data could be available.
W
Workflows
Workflows are the pieces of an automation project that, when combined, make a complete automation. These are reusable and are considered to be the building blocks of an automation project. Workflows are basically small blocks of automation (or small bots) which can be embedded in other automations. Talking an example from the UiPath tool – we can have the following kinds of workflows:
Sequences: Sequences are the simplest kind of workflow and are linear in nature. There are no decision blocks involved and the flow is executed one piece after other. For example: Get the user date of birth, calculate the age, and display the age.
Flowchart: Flowcharts are the kind of workflows which provides a two-dimensional layout. We can have decision blocks and the flow of automation is decided based on the decision points. For example: Get the user date of birth, calculate the age, check if age is less than or greater than 18, and decide if the user is eligible to vote or not.
State Machine: State Machine is a complex workflow type suited for transactional processes. We have called transitions that helps us to maintain the flow of execution. A state machine uses a finite number of states in its execution and can have more than one state to build complex automations. A classic example of state machine is UiPath robotic enterprise framework.
Global Exception Handler: The Exception handler is a workflow designed to identify execution errors and is designed to be used for both small- and large-scale deployments. Depending upon the exception type the next behavior of the automation can be controlled.
Get a FREE quote on your project today!
Your idea is 100% protected by our Non-Disclosure Agreement
Related Posts
5 Pillars of your Generative AI Application
Organizations are actively looking for ways to improve the productivity and efficiency of their company. With the arrival of generative AI,…
5 Mistakes to Avoid in Generative AI Application
Did you know that, according to HubSpot with customer service chatbots, businesses can save 2 hours 20 minutes daily? Generative AI…
5 Rules to Follow for LangChain Generative AI Application
According to the latest Gartner reports, generative AI adoption in organizations could increase productivity by 24.69%. Developing…
You might also like
Stay ahead in tech with Sunflower Lab’s curated blogs, sorted by technology type. From AI to Digital Products, explore cutting-edge developments in our insightful, categorized collection. Dive in and stay informed about the ever-evolving digital landscape with Sunflower Lab.








